what is hydrolyzed protein

The Truth Behind Hydrolysed Protein | What Is It Good For?
When did buying protein get flooded with so much choice? And even the good old trusty whey protein has now been broken down into different types! However, each one has a specific process in the body and can fuel your workouts in a different way. We can appreciate that it might sound a bit scientific, but hydrolysed protein is an excellent form of protein to use. This article will give you the lowdown on hydrolysed protein, including what it is, what it does and what it's good for.
What Does Hydrolysed Mean?
So, lets start with what hydrolysed protein actually is. Hydrolysed means that the protein has been partially broken down, making it more easy to digest. Some people refer to it as pre-digested, which sounds a bit gross, however, that doesn't mean that another person has digested your protein before you!
The process of hydrolysing simply involves adding proteolytic enzymes when making the powder, which will increase the speed your body can transport the amino acids to your muscles. This causes an increase in protein synthesis from an increase in amino acids reaching your muscles, which causes the muscle fibres to rebuild faster, to get you refuelled in time for your next workout.
Can You Get Hydrolysed Vegetable Protein?
Hydrolysed protein seems to be most popular in whey and casein variations, although some vegetable proteins have started to go through a similar process. However, there seems to be a longer process to break down the proteins and the use of chemicals make it less beneficial for the general user looking to rebuild muscles. Therefore, vegetable protein blends contain a vegetable isolate version with added digestion enzymes in the blend.
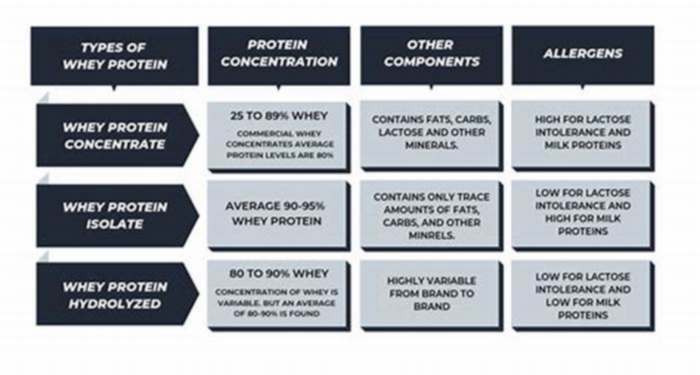
Hydrolysed Protein vs. Isolate
Now, in comparison to other forms of whey, hydrolysed whey protein has a higher percentage of leucine content compared to isolate and concentrate. Leucine has been linked to the regeneration of muscle fibres and particularly increases in muscle size and density. It also prevents muscle breakdown even when you're in a calorie deficit.
Heres where it gets really interesting: when casein protein goes through the hydrolysing process, it acts a little more like whey protein in terms of speed of muscle-protein synthesis as well as keeping its high-yielding, long-release properties we all know and love. Its also been found to improve endurance exercise performance when combined with fast-acting carbohydrates, making athletes faster when its taken during a session [1].
Recent research (2010) has found that whey hydrolysate (hydrolysed whey) was better than whey isolate when it came to a faster recovery from a high intensity muscle damage protocol [2]. This would mean that if you're looking for a speedy recovery between training sessions, or before a long day at work, hydrolysed whey could be the way to go. Interestingly, when this was taken further and analysed for insulin response, the hydrolysed version gave an increased response [3].
If you dont know much about insulin in the body, the hormone causes the nutrients in the blood stream to be forced into storage areas i.e. the free amino acids in the blood get pushed into the muscles where they can be used, stored and give you a great boost in muscle size and density.
Additional Benefits of Hydrolysed Protein
The benefits of hydrolysed protein go further than muscle building alone. Hydrolysed collagen protein can go a long way to look after the rest of your body, including your hair, skin, and joints. The broken down amino acids from the hydrolysing process can help to enrich the components that make up the rest of your body parts of which are made up of collagen which cannot be replenished without dietary intake. As you use some of cleansing products to your hair and skin, this can dry out the skin, where collagen intake can push the lift back into you.
From a performance point of view, hydrolysed collagen protein can improve your joints and reduce the likelihood of injury by keeping the ligaments and tendons strong.
Take Home Message
At the end of the day, the most important factor is increasing the daily protein intake to meet required levels, however, supplementing your diet with hydrolysed protein can help you to: improve the speed of your recovery, which is important if you are training multiple times per day (whey); improve your intra-workout performance (casein); improve your hair, joints, nails and skin (collagen).
Hydrolyzed Protein: Understanding the Process and Benefits
Hydrolyzed Protein: Understanding the Process and Benefits
Hydrolyzed protein has been gaining in popularity among athletes and fitness enthusiasts as a highly effective source of protein for muscle building and recovery. This article will delve into the process of hydrolysis, how it is produced, the different types of hydrolyzed protein, and the benefits of consumption. Additionally, we will explore the scientific studies on the efficacy of hydrolyzed protein and potential side effects. Finally, experts will share their opinions on the safety and effectiveness of consuming hydrolyzed protein and provide some recipe ideas for healthy meals and snacks.
What is Hydrolyzed Protein and How is it Produced?
Hydrolyzed protein is a type of protein powder that is created by breaking down large protein molecules into smaller peptide chains, which are easier for the body to digest and utilize. This process is called hydrolysis, and it involves the use of enzymes or acid to denature the protein and break it down into smaller fractions.
Hydrolyzed protein can be produced from a variety of sources, including whey, casein, soy, and collagen. The source of the protein can impact the nutritional profile and amino acid composition of the resulting hydrolyzed protein powder. Hydrolyzed whey protein, for example, is high in branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs), which are essential for muscle growth and recovery.
Hydrolyzed protein is commonly used in sports nutrition supplements, as it is absorbed more quickly by the body than other forms of protein. This makes it an ideal choice for athletes and bodybuilders who need to quickly replenish their muscles after a workout. Additionally, hydrolyzed protein is often used in medical nutrition products, as it is easier for people with digestive issues to tolerate and absorb.
The Science Behind Hydrolysis: Breaking Down Protein Molecules
Hydrolysis is a chemical process that involves breaking down large protein molecules into smaller peptide chains. This process can occur naturally through the action of digestive enzymes in the stomach and small intestine, or it can be induced through the use of enzymes or acid during the manufacturing process.
The goal of hydrolysis is to reduce the size of the protein molecules, which can improve the digestion and absorption of the protein into the body. Hydrolyzed protein is essentially a pre-digested form of protein that requires less energy and digestive enzymes to break down and utilize compared to intact protein.
Hydrolysis is commonly used in the food industry to improve the nutritional value and functionality of protein-rich foods. For example, hydrolyzed whey protein is often added to sports supplements and protein bars to enhance their amino acid profile and improve their digestibility.
However, it's important to note that not all hydrolyzed proteins are created equal. The degree of hydrolysis, or the extent to which the protein is broken down, can vary depending on the manufacturing process and the specific enzyme or acid used. This can affect the quality and bioavailability of the resulting hydrolyzed protein.
Types of Hydrolyzed Protein: Whey, Casein, Soy, and More
Hydrolyzed protein can be produced from a variety of sources, including whey, casein, soy, and collagen. Each source of protein will have a distinct nutritional profile and amino acid composition, which can impact the effectiveness of the hydrolyzed protein for different purposes. For example, hydrolyzed whey protein is popular among athletes and bodybuilders due to its high BCAA content, while hydrolyzed collagen is often used for skin and joint health due to its high concentration of glycine and proline.
Other types of hydrolyzed protein include:
- Hydrolyzed casein protein
- Hydrolyzed soy protein
- Hydrolyzed beef protein
- Hydrolyzed pea protein
Each type of hydrolyzed protein has unique benefits and applications, and it is important to consider your individual goals and preferences when selecting a product.
Hydrolyzed whey protein is a popular choice for those looking to build muscle mass and improve athletic performance. This is because it is quickly absorbed by the body, providing a fast source of amino acids to support muscle growth and repair. In addition, hydrolyzed whey protein is often low in lactose, making it a good option for those with lactose intolerance.
Hydrolyzed soy protein, on the other hand, is a good choice for vegetarians and vegans looking to supplement their protein intake. Soy protein is a complete protein, meaning it contains all nine essential amino acids that the body cannot produce on its own. It is also a good source of antioxidants and has been shown to have potential health benefits, such as reducing cholesterol levels and improving heart health.
Differences Between Hydrolyzed and Regular Protein Powders
Hydrolyzed protein differs from regular protein powders in a few key ways. First, hydrolyzed protein has undergone a chemical process to break down the protein molecules into smaller peptides, while regular protein powders are typically made by removing the fat and carbohydrate components of the protein source.
Additionally, hydrolyzed protein is pre-digested, which means it requires less energy and digestive enzymes to break down and utilize compared to regular protein powders. Hydrolyzed protein is also typically faster-absorbing than regular protein powders, which can make it a better choice for post-workout recovery or other times when rapid absorption is desired.
Benefits of Hydrolyzed Protein for Muscle Building and Recovery
Hydrolyzed protein is a highly effective source of protein for muscle building and recovery due to its rapid absorption and high concentration of BCAAs. BCAAs are essential amino acids that play a crucial role in muscle protein synthesis and repair. Consuming hydrolyzed protein after a workout can help to stimulate muscle protein synthesis and enhance recovery.
Additionally, hydrolyzed protein may be useful for individuals with compromised digestive function, as it is pre-digested and requires less energy to break down and utilize. This can be especially beneficial for older adults or individuals with digestive disorders.
Hydrolyzed Protein and Digestion: Improved Absorption and Gut Health
Hydrolyzed protein may also offer benefits for gut health and digestion. The smaller peptides in hydrolyzed protein are less likely to cause digestive discomfort or bloating compared to intact protein, making it a better choice for individuals with sensitive digestive systems.
Hydrolyzed protein may also help to improve the absorption of other nutrients, such as carbohydrates and fats. This can be particularly beneficial for athletes and active individuals who need to replenish glycogen stores and support overall energy balance.
How to Incorporate Hydrolyzed Protein into Your Diet and Training Regimen
Hydrolyzed protein can be incorporated into your diet and training regimen in a variety of ways. It can be consumed post-workout in a shake or smoothie, or it can be added to meals or snacks throughout the day to increase your overall protein intake. You can also try using hydrolyzed protein in baking or cooking to create protein-packed snacks and meals.
It is important to follow the recommended dosage on the product label when consuming hydrolyzed protein, as excessive consumption may lead to adverse effects such as digestive discomfort or kidney damage.
Potential Side Effects of Consuming Hydrolyzed Protein
While hydrolyzed protein is generally safe to consume for most individuals, it is important to be aware of potential side effects. Excessive consumption of hydrolyzed protein may lead to digestive discomfort, including bloating, gas, and diarrhea. Additionally, individuals with kidney disease may need to limit their intake of protein, including hydrolyzed protein, to avoid further damage to the kidneys.
Choosing the Best Hydrolyzed Protein Supplement for Your Goals
When selecting a hydrolyzed protein supplement, it is important to consider your individual goals and preferences. Look for a product that is made from a high-quality protein source and has undergone a reputable hydrolysis process. Additionally, consider the taste and texture of the product, as well as any added ingredients or flavors that may impact your overall nutrition intake.
Finally, be sure to follow the recommended dosage on the product label and seek advice from a healthcare professional if you have any concerns or underlying health conditions.
Scientific Studies on the Efficacy of Hydrolyzed Protein for Athletic Performance
There have been several scientific studies investigating the efficacy of hydrolyzed protein for athletic performance. One study found that hydrolyzed whey protein led to greater muscle protein synthesis compared to intact whey protein, suggesting that hydrolysis may enhance the effects of protein for muscle building and repair.
Another study found that consuming hydrolyzed collagen improved joint mobility and reduced joint pain in athletes, suggesting that hydrolyzed protein may have additional benefits for supporting overall joint health and mobility.
Comparing the Cost of Hydrolyzed Protein Supplements to Other Sources of Protein
Hydrolyzed protein supplements can be more expensive than other sources of protein, such as whole food sources or regular protein powders. However, the rapid absorption and high concentration of BCAAs in hydrolyzed protein may make it a more effective source of protein for muscle building and recovery, which may justify the higher cost.
Ultimately, the cost of hydrolyzed protein supplements will depend on the brand, quality, and type of protein used. It is important to consider your budget and individual goals when selecting a protein source.
Common Misconceptions About Hydrolyzed Protein: Debunking Myths
There are several common misconceptions about hydrolyzed protein that may be perpetuated in the fitness and supplement industries. One myth is that hydrolyzed protein is automatically superior to other protein sources, when in reality each protein source has its own unique benefits and applications.
Additionally, some may believe that hydrolyzed protein is necessary for muscle building and recovery, when in reality a well-balanced diet that includes a variety of protein sources can be just as effective in supporting muscle growth and repair.
Expert Opinions on the Safety and Effectiveness of Consuming Hydrolyzed Protein
Experts in the sports nutrition and fitness industry generally agree that hydrolyzed protein can be a highly effective source of protein for muscle building and recovery. However, it is important to select a high-quality product and follow the recommended dosage to avoid potential adverse effects.
Some experts also caution against relying too heavily on supplements for nutritional needs, instead emphasizing the importance of a well-balanced diet that includes a variety of whole food protein sources.
Cooking with Hydrolyzed Protein: Recipe Ideas for Healthy Meals and Snacks
Hydrolyzed protein can be a versatile ingredient in cooking and baking, allowing you to boost the protein content of your favorite meals and snacks. Consider adding hydrolyzed protein to smoothies, oatmeal, yogurt, or baked goods for a protein-packed treat.
Here are some recipe ideas:
- Chocolate protein pancakes: This recipe combines banana, oats, and chocolate hydrolyzed whey protein for a delicious and protein-packed breakfast treat.
- Protein-packed smoothie bowl: Combine your favorite fruits and veggies with hydrolyzed protein powder for a filling and nutritious breakfast or snack.
- Peanut butter protein cookies: These cookies are made with hydrolyzed casein protein and naturally sweetened with bananas and peanut butter.
Experiment with different types of hydrolyzed protein and cooking methods to find what works best for you and your taste preferences.
In conclusion, hydrolyzed protein is a highly effective source of protein for muscle building and recovery due to its rapid absorption and high concentration of BCAAs and other essential amino acids. There are many different types of hydrolyzed protein, each with their own unique benefits and applications. It is important to choose a high-quality product and follow the recommended dosage to avoid potential adverse effects. Additionally, experts caution against relying too heavily on supplements for nutritional needs and emphasize the importance of a well-balanced diet that includes a variety of whole food protein sources.